Celiac disease resource center
What is celiac disease?
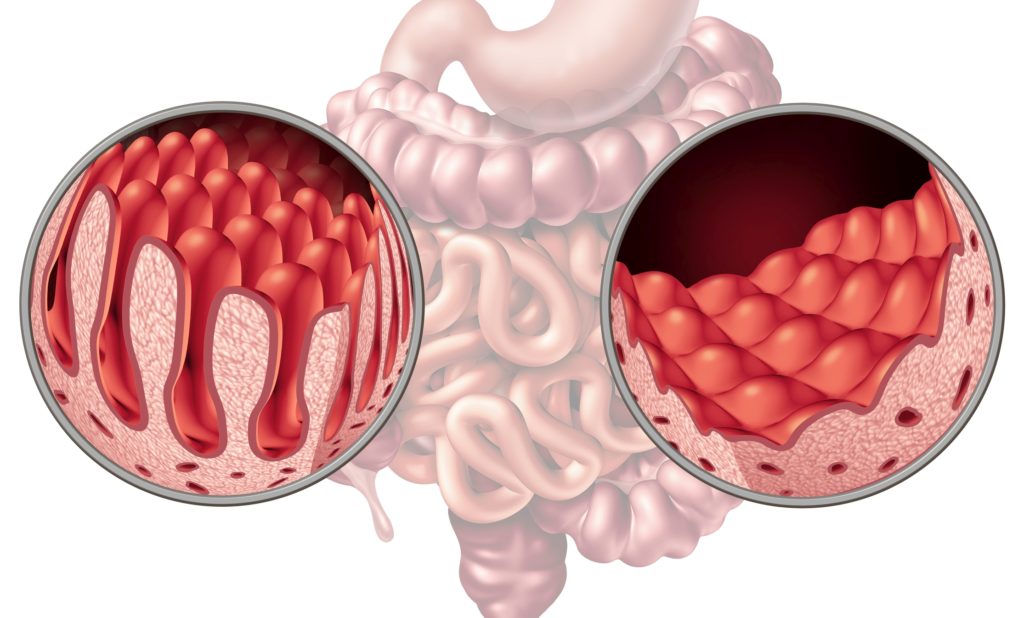
Celiac disease is a condition that happens when a person develops inflammation, or swelling, and damage to their intestine (gut) when they eat gluten. When a person with celiac disease eats gluten, the immune system, which is supposed to help protect the body against disease, reacts by hurting the cells lining the small intestine and may also harm other parts of the body such as the skin, bones or brain (nervous system).
Celiac disease: From discovery to clinical practice
A recent special issue of the AGA journal Gastroenterology focuses on celiac disease. The articles look at what is already known about celiac disease to help patients, their health care providers and researchers better understand and learn more about this autoimmune condition, which affects more than 3 million people in the U.S. This special edition highlights how our understanding of celiac disease has grown quickly after a long period of slow progress.
AGA presents the following articles written by Beyond Celiac to help patients and health care providers better understand the future of celiac disease research which hopes to bring new ways to diagnose, prevent and maybe even treat the condition using methods that don’t involve a gluten-free diet.
- Are we ready for an approved celiac disease treatment?
- Celiac disease: Who should be tested
- Celiac disease is no longer thought to only affect the gut
- Cost of gluten-free food is just the tip of the iceberg of economic burden of celiac disease
- Healthy gluten-free diet requires careful, consistent nutritional follow-up



