Iron deficiency anemia
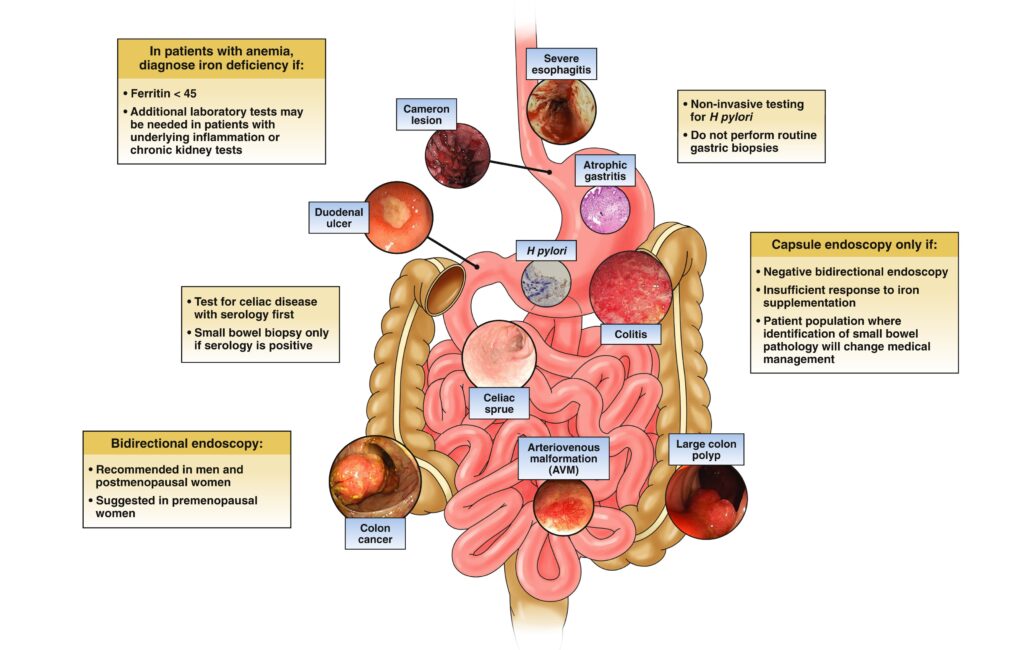
Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia that happens when you don’t have enough iron to make healthy red blood cells.
Colonoscopy
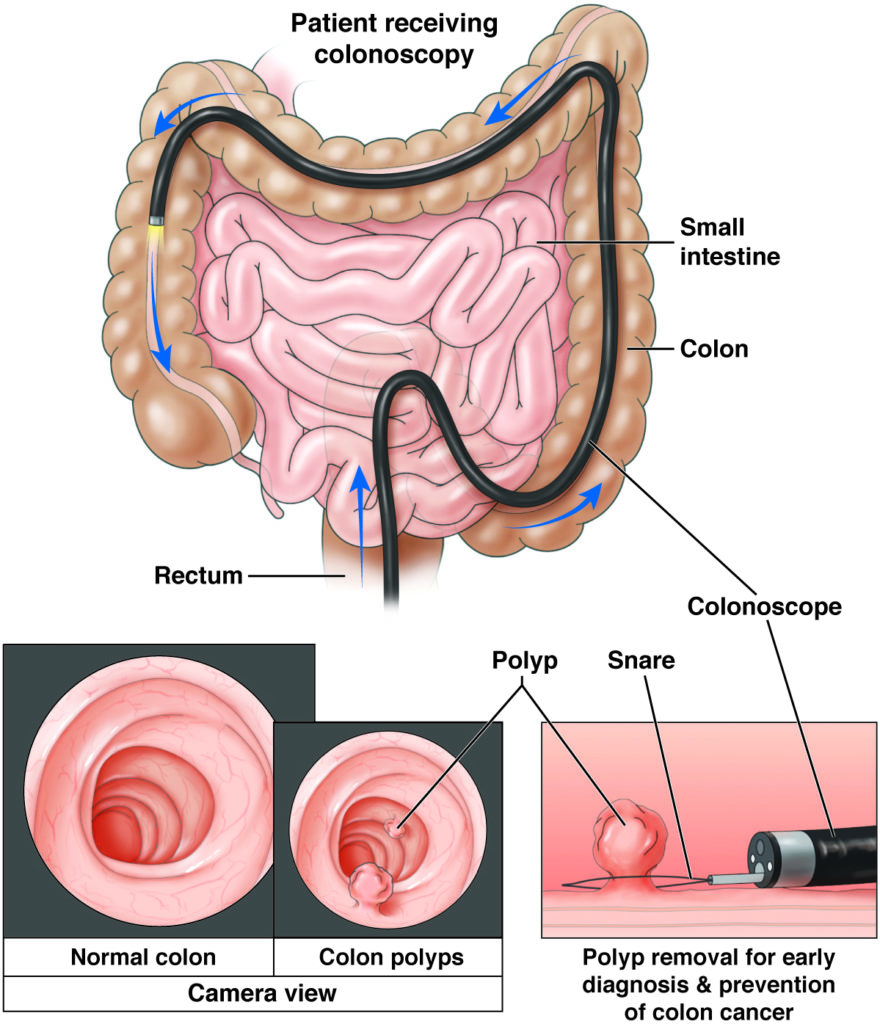
A colonoscopy is a procedure performed by a doctor called a gastroenterologist, who uses a colonoscope to look inside the colon and check for diseases like cancer or colitis.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Vaccine recommendations
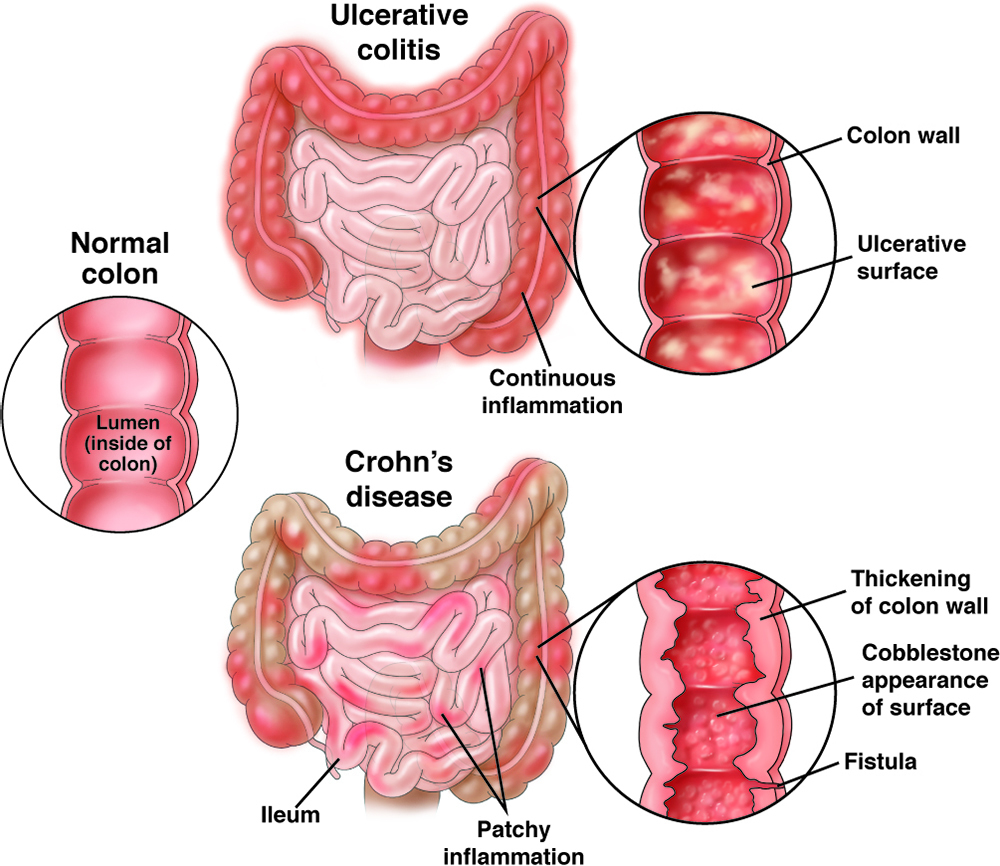
Patients with IBD need to work with their health care providers to decide which vaccines they need to stay healthy.
Colorectal cancer screening: What to expect when paying
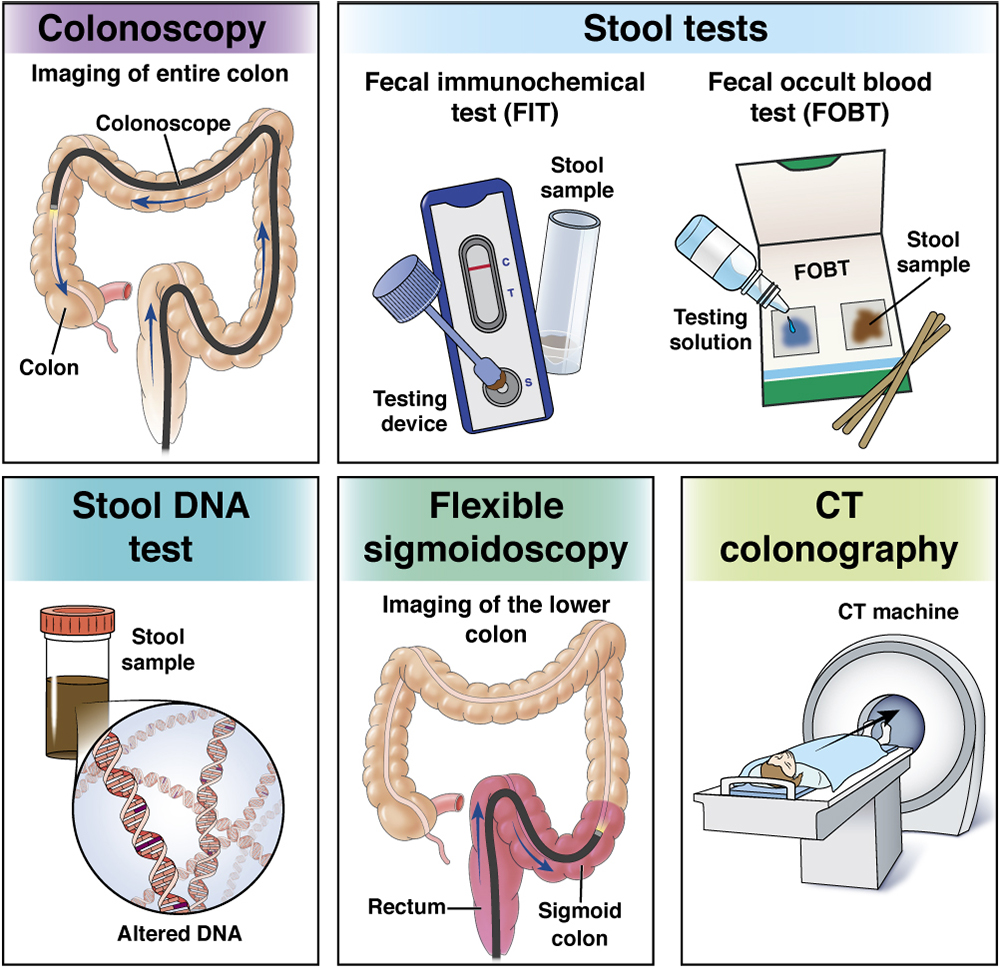
Learn what to expect and what to do if you get a bill you were not expecting after having a colorectal cancer screening.
Crohn’s disease: exclusive enteral nutrition
Exclusive enteral nutrition, or EEN, is a low risk and safe therapy that can help improve symptoms of Crohn’s disease.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Role of fiber
Consuming a wide variety of foods with fiber is important for gut health in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Diet tips
Diet tips to help reduce symptoms during Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis flares or active disease.
Gentle GI nutrition
Also called the non-diet approach, this approach focuses on finding alternatives besides restrictive diets to help with GI symptoms.
Clostridioides difficile (C. diff)
Clostridioides difficile, or C. diff, is a bacterium that can cause gastrointestinal symptoms, like nausea, watery diarrhea, stomach pain and stomach cramps that may be severe.
Biosimilars
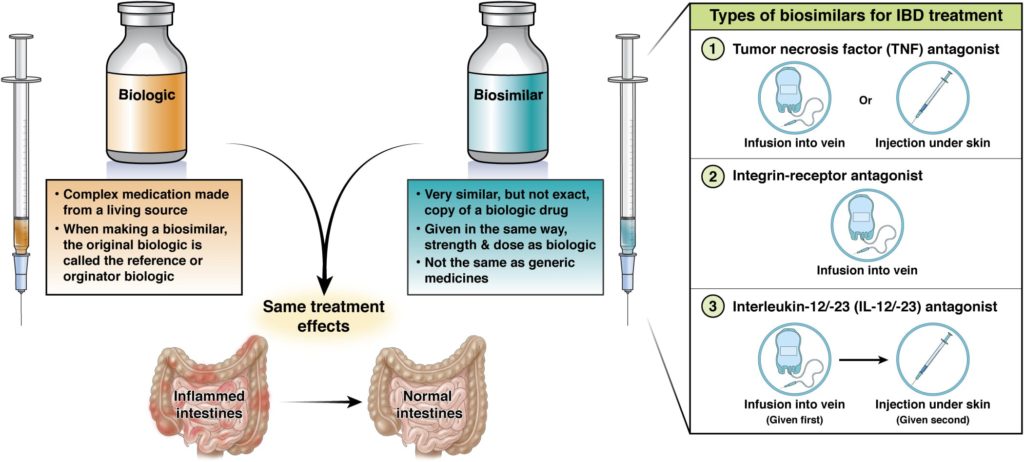
Biosimilars are a type of biologic. Biologics and biosimilars can help patients with moderate to severe IBD.


