Obesity: Learn the facts beyond the scale for Hispanic Americans
Obesity is a disease that impacts some ethnic and racial groups more than others, including nearly half of Hispanic American adults.
Brought to you by the American Gastroenterological Association

Obesity is a disease that impacts some ethnic and racial groups more than others, including nearly half of Hispanic American adults.
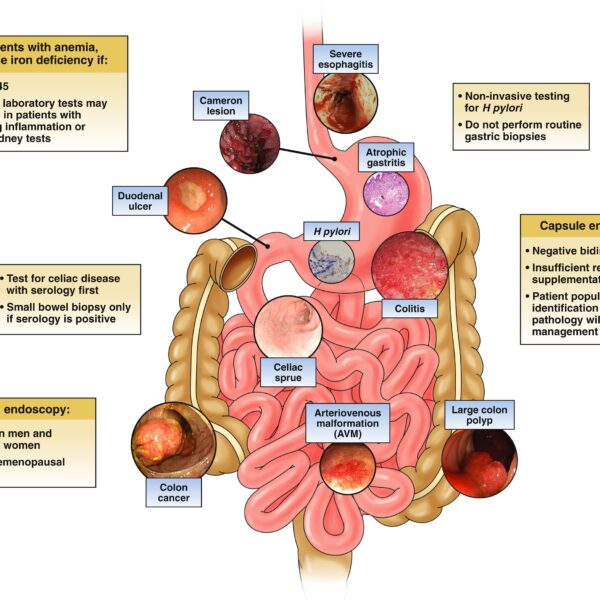
Iron deficiency anemia is the most common type of anemia that happens when you don’t have enough iron to make healthy red blood cells.

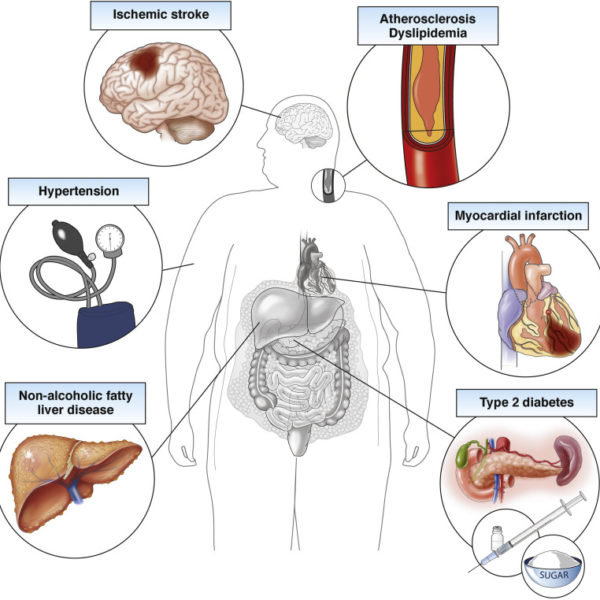
Obesity is a chronic disease in which someone has an excess of fat that negatively impacts their health. The calculation of body mass index (BMI) is typically used to measure if someone has obesity (overweight).

Obesity is a chronic disease in which someone has an excess of fat that negatively impacts their health. The calculation of body mass index (BMI) is typically used to measure if someone has obesity (overweight).

Obesity is a chronic disease in which someone has an excess of fat that negatively impacts their health. The calculation of body mass index (BMI) is typically used to measure if someone has obesity (overweight).
Health At Every Size, or HAES, is a weight-neutral approach to health, independent of weight that can help you achieve health and well-being.
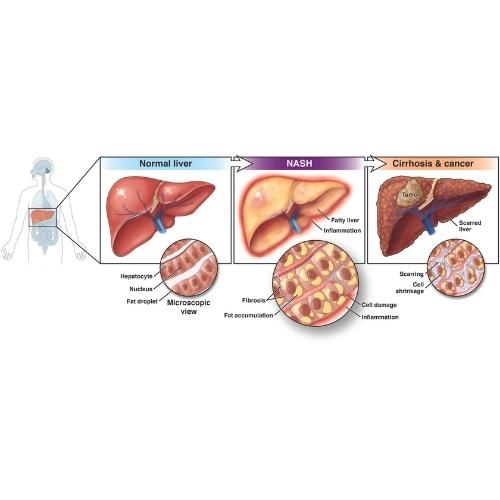
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) happens when your liver stores too much fat and it is not related to heavy alcohol use. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH, is a more severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that causes inflammation, called hepatitis, and liver cell damage.
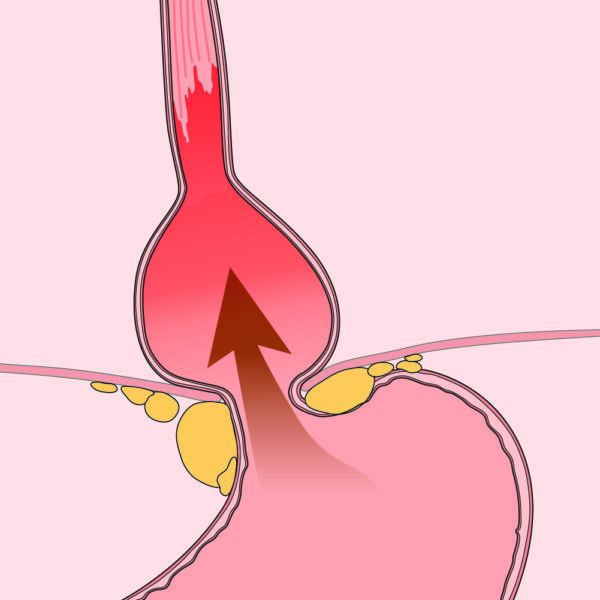
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or just acid reflux, is when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus. Heartburn is the most common symptom of GERD.
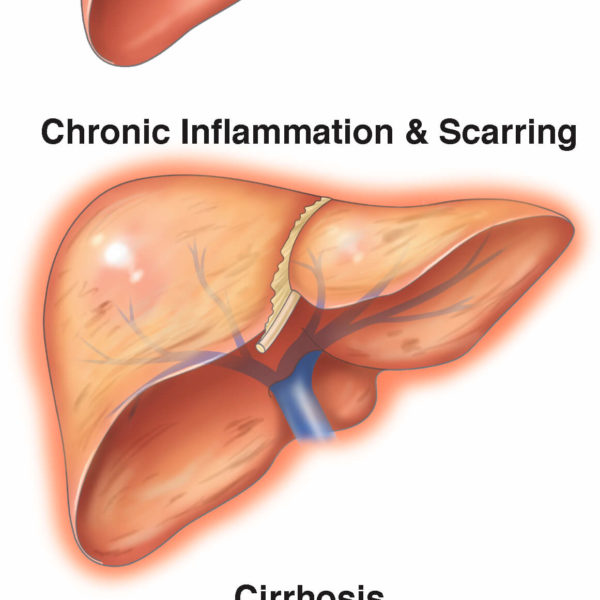
Cirrhosis is permanent damage to the liver by chronic diseases, such as viral hepatitis, NAFLD or long-term alcohol abuse.
4930 Del Ray Avenue
Bethesda, MD 20814
301-654-2055
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
This website uses Google Analytics to collect anonymous information such as the number of visitors to the site, and the most popular pages.
Keeping this cookie enabled helps us to improve our website.
Please enable Strictly Necessary Cookies first so that we can save your preferences!