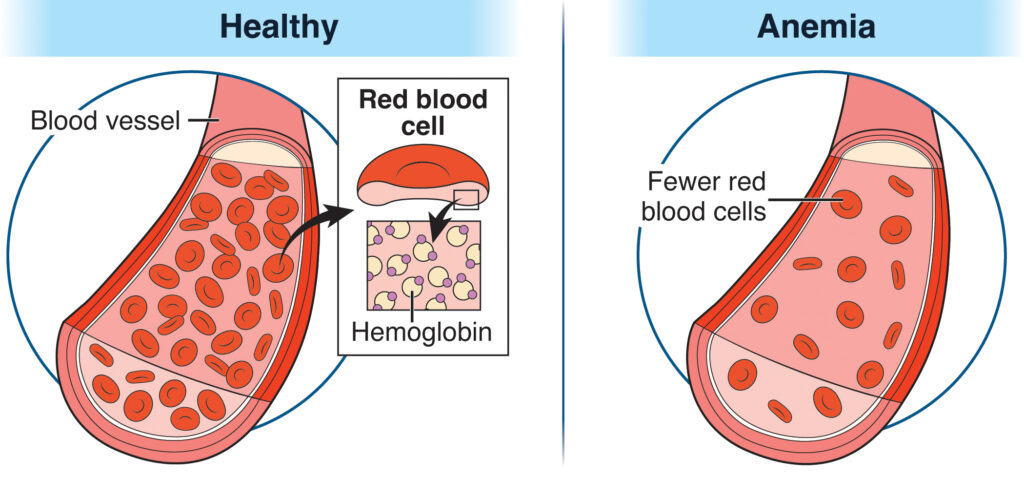
- Iron deficiency anemia is when you have low blood count (low hemoglobin) and not enough iron in your blood.
- A normal iron level is important to make healthy read blood cells.
Who is affected?
- Anyone can have iron deficiency anemia.
- It can develop in people of all ages, genders, races and ethnicities.
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia

Why is iron deficiency anemia serious?
- Iron deficiency anemia can be a sign of gastroenterological (GI) cancer or conditions that can cause severe complications if left untreated.
Common causes
-
Not eating enough foods with iron
- Vegan/vegetarian diet
- Diet low in foods like leafy green vegetables, eggs and meat
-
Problems absorbing the iron from food that you eat through your gastointestinal (GI, digestive) system
- Celiac disease
- Gastric bypass surgery
- Removal of part of your small intestine
-
Too much blood loss
- This is most common in women who are menstruating (have their period) or pregnant. Heavier-than-usual periods over time can lead to low blood count.
- Ulcers (sores) or inflammation (swelling) in the lining of your GI tract. You may not see blood in your stool, but these may bleed over time in very small amounts and cause a low blood count.
- Cancer or pre-cancerous polyps (a cancerous growth inside of the colon or rectum) in the GI tract. You may not see blood in your stool, but these may bleed over time in very small amounts and cause a low blood count.
- Inflammatory bowel disease, (IBD), such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, when there is inflammation in the GI tract.
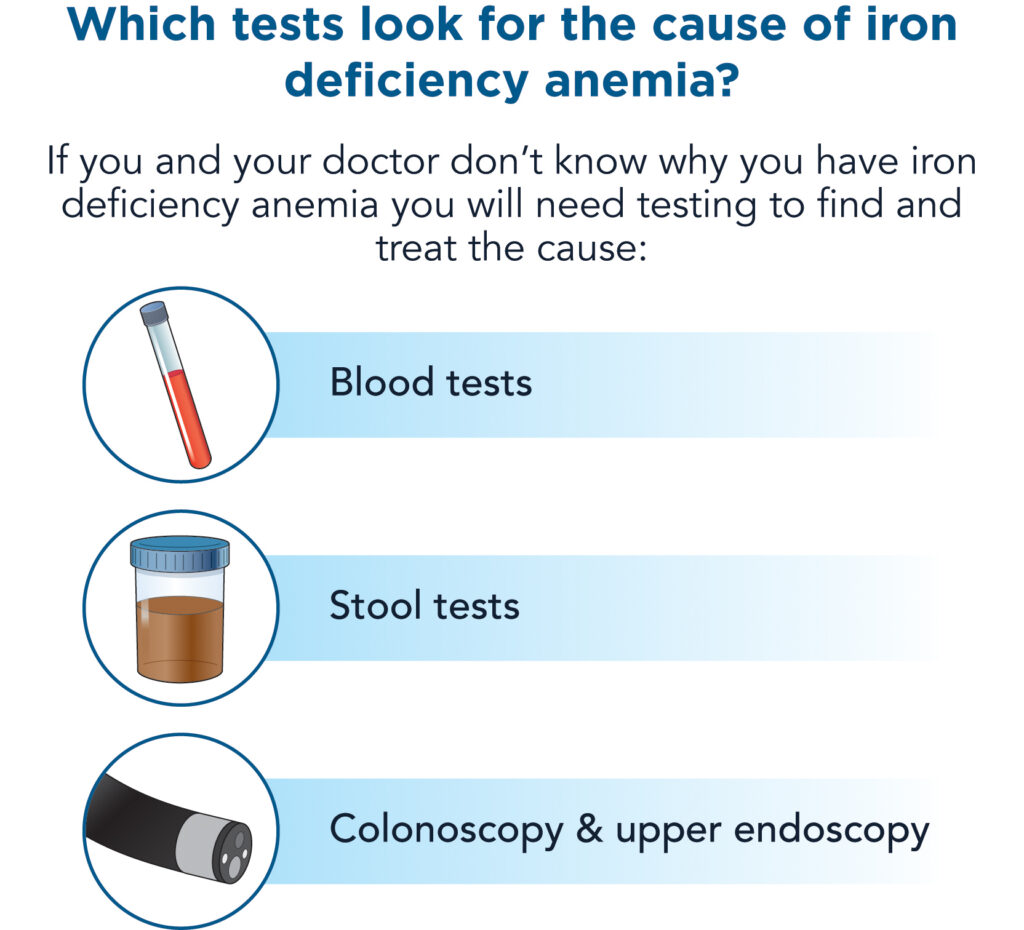
Testing for the cause of iron deficiency anemia
How is iron deficiency diagnosed?
- Iron deficiency anemia is diagnosed by routine blood tests that measure your red blood count.
- These blood tests can be ordered by your health care provider.

What do I have to do before a colonoscopy and upper endoscopy?
These are procedures that allow for direct exam of the GI tract. Talk to your health care provider and ask if any of your medications need to be stopped before your procedure. You will be given medicine right before both procedures to make you sleepy and relaxed.
- For colonoscopy, drink clear liquids the day before your procedure. Drink laxatives that will help you move your bowels and clean out your colon before the procedure. Be sure to follow all of your doctor’s instructions.
- For upper endoscopy, don’t eat or drink anything for at least 12 hours before your procedure.
Colonoscopy
During a colonoscopy, the doctor will insert a scope into your rectum to look carefully in your colon for any cause of your iron deficiency anemia, like cancer or polyps.
Upper endoscopy (EGD)
An upper endoscopy is done using a shorter scope which is put into your mouth to look for ulcers or swelling at the beginning portion of your GI tract.
Treatments for iron deficiency anemia

Last updated: July 2024



